
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. The successor to Windows 8.1, it was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, to retail on July 29, 2015, and was a free upgrade to users of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1. Its server counterparts are Windows Server 2016, 2019, and 2022. It was succeeded by Windows 11 in October 2021.
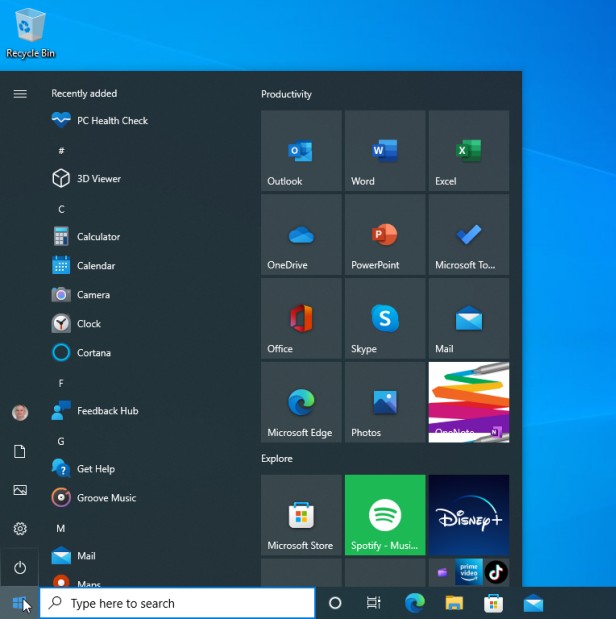
In contrast to the tablet-oriented approach of its predecessor, Windows 10 returned to a desktop-oriented interface in line with previous versions of Windows and reintroduced the Start menu. Other features included the Cortana virtual assistant, Task View and virtual desktops, Action Center, biometric authentication through Windows Hello, an improved Settings component, Xbox Live integration, and DirectX 12. Also, Microsoft Edge was introduced, deprecating Internet Explorer. Unlike previous NT releases, Windows 10 received free feature updates on an ongoing basis. Alternatively, enterprise environments can use long-term support milestones that receive only critical and security updates. An ARM version of Windows 10 was released in 2018.
Windows 10 received generally positive reviews. Praise was given to the return of the desktop interface, improved bundled software compared to Windows 8.1, and other capabilities, while criticism was directed at behavioral changes such as mandatory update installation, privacy concerns over data collection, and adware-like tactics to promote the operating system on release. Microsoft aimed to have Windows 10 installed on over a billion devices within three years of release; ultimately, that goal was reached in March 2020, almost five years later. By January 2018, it surpassed Windows 7 as the most popular version of Windows worldwide, until Windows 11 took the top spot in June 2025. As of November 2025, Windows 10 is the second-most-used version of Windows, accounting for 42.62% worldwide share, while Windows 11 holds 55%. As of December 2025, an estimated 1 billion PCs globally are running Windows 10.
It is the last version of Windows that supports 32-bit processors, BIOS firmware, and systems with no TPM or TPM 1.2; it is also the last to officially lack a CPU model check before installation. Support ended on October 14, 2025, except for editions in the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) or enrolled in the Extended Security Updates program.